Matters of the heart can be complicated, but York University scientists have found a way to create 3D heart tissue that beats in synchronized harmony, like a heart in love, that will lead to better understanding of cardiac health, and improved treatments.
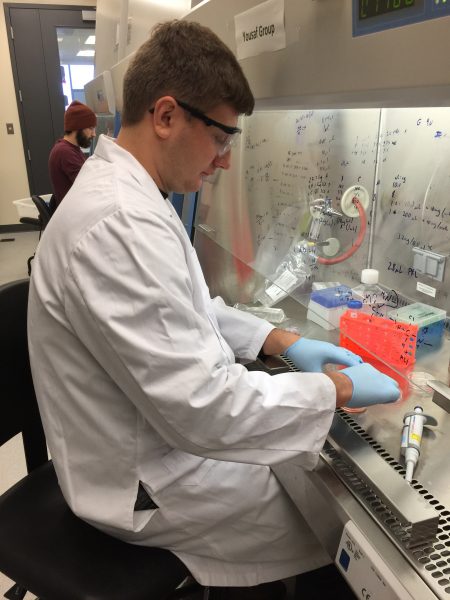 Dmitry Rogozhnikov, a chemistry PhD student at York, in the lab creating a 3D heart
Dmitry Rogozhnikov, a chemistry PhD student at York, in the lab creating a 3D heart
York U chemistry Professor Muhammad Yousaf and his team of grad students have devised a way to stick three different types of cardiac cells together, like Velcro, to make heart tissue that beats as one.
Until now, most 2D and 3D in vitro tissue did not beat in harmony and required scaffolding for the cells to hold onto and grow, causing limitations. In this research, Yousaf and his team made a scaffold free beating tissue out of three cell types found in the heart – contractile cardiac muscle cells, connective tissue cells and vascular cells.
The researchers believe this is the first 3D in vitro cardiac tissue with three cell types that can beat together as one entity rather than at different intervals.
“This breakthrough will allow better and earlier drug testing, and potentially eliminate harmful or toxic medications sooner,” said Yousaf of York U’s Faculty of Science.
In addition, the substance used to stick cells together (ViaGlue), will provide researchers with tools to create and test 3D in vitro cardiac tissue in their own labs to study heart disease and issues with transplantation. Cardiovascular associated diseases are the leading cause of death globally and are responsible for 40 per cent of deaths in North America.
“Making in vitro 3D cardiac tissue has long presented a challenge to scientists because of the high density of cells and muscularity of the heart,” said Dmitry Rogozhnikov, a chemistry PhD student at York. “For 2D or 3D cardiac tissue to be functional it needs the same high cellular density and the cells must be in contact to facilitate synchronized beating.”

Although the 3D cardiac tissue was created at a millimeter scale, larger versions could be made, said Yousaf, who has created a start-up company OrganoLinX to commercialize the ViaGlue reagent and to provide custom 3D tissues on demand.
The study, “Scaffold Free Bio-orthogonal Assembly of 3-Dimensional Cardiac Tissue via Cell Surface Engineering,” was published in Nature Scientific Reports.
York University is known for championing new ways of thinking that drive teaching and research excellence. Our students receive the education they need to create big ideas that make an impact on the world. Meaningful and sometimes unexpected careers result from cross-discipline programming, innovative course design and diverse experiential learning opportunities. York students and graduates push limits, achieve goals and find solutions to the world’s most pressing social challenges, empowered by a strong community that opens minds. York U is an internationally recognized research university – our 11 faculties and 26 research centres have partnerships with 200+ leading universities worldwide. Located in Toronto, York is the third largest university in Canada, with a strong community of 53,000 students, 7,000 faculty and administrative staff, and more than 295,000 alumni. York U’s fully bilingual Glendon campus is home to Southern Ontario’s Centre of Excellence for French Language and Bilingual Postsecondary Education.