[tta_listen_btn listen_text=”Click to listen to this story” pause_text=”Pause” resume_text=”Resume” replay_text=”Replay” start_text=”Start” stop_text=”Stop”]
A research paper by master’s student Ethan Owen, from York University’s Faculty of Science, was recently published in the journal Biodiversity and Conservation. Titled “The importance of native shrubs on the distribution and diversity of reptiles and amphibians in the central drylands of Southwestern USA,” Owen’s first-ever published study involved scouring 43 sites across California’s deserts with his team to understand how the density of native shrubs affects local wildlife.
Armed with high-resolution satellite images and citizen science data sourced from the Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) – an international, open-access network and data infrastructure funded by the world’s governments – the researchers set out to uncover hidden patterns in these rugged landscapes.
The team’s findings showed that areas with higher shrub density had significantly more abundant, rich, and diverse reptile and amphibian communities, proving the shrubs are indispensable for the creatures’ survival by creating microhabitats that offer cooler temperatures and crucial hiding spots.
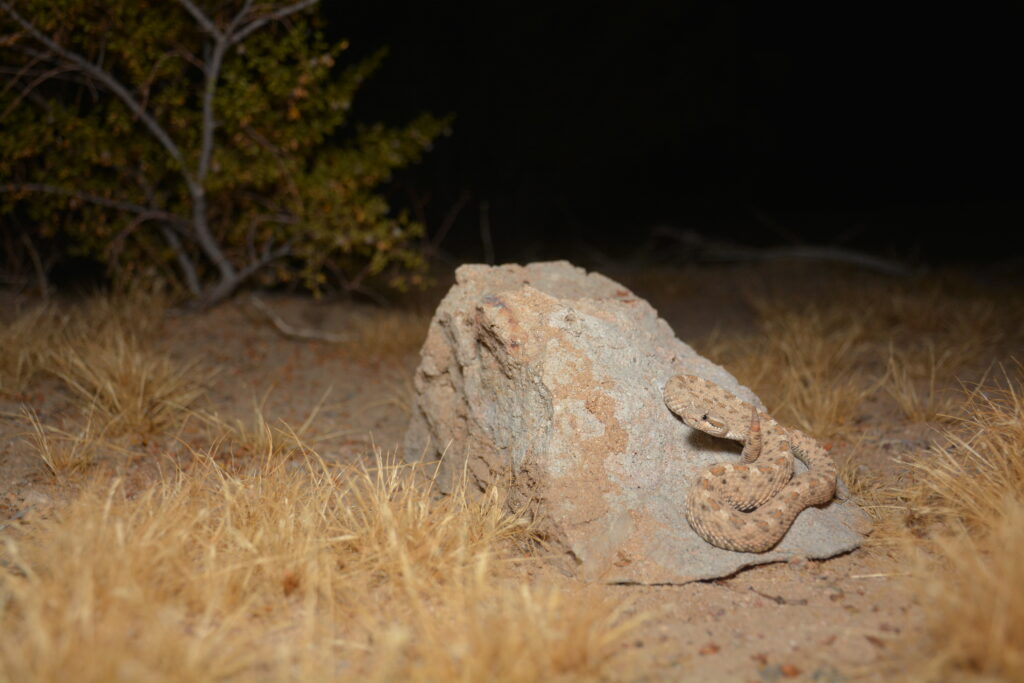

“These shrubs are more than just plants; they are lifelines,” explains Owen. “In the central drylands of California, they provide essential shelter, food, and protection for a variety of reptile and amphibian species, helping them survive the extreme conditions.”
But the study didn’t stop at counting reptiles and amphibians. Owen’s team looked at different levels of aridity to see if the relationship held up. “It was fascinating to see that regardless of how dry the area was, the presence of these shrubs consistently boosted the diversity and abundance of the local wildlife,” he says. “It really underscores their importance in these arid ecosystems.”
Owen believes the implications of this research are profound, offering valuable insights for conservationists and land managers alike. “By maintaining and promoting native shrub species, we can support biodiversity, even in the face of climate change,” he says.
As the natural world continues to suffer the consequences of global warming, Owen hopes that research like his will serve as a reminder that even small interventions – like protecting existing shrubs or planting new ones – can have significant positive impacts on the health and diversity of the Earth’s ecosystems.