Alexandro Di Nunzio, a Digital Media master’s student, is currently on exchange at Bauhaus University in Weimar, Germany, after being awarded a five-month scholarship as part of the Erasmus+ KA171 DAAD programme. His primary research focus while abroad is in the development of multiplayer virtual reality applications in the Unity Game Engine, utilizing the ‘vrEDUsys’ multi-user framework being developed and shared by researchers at Bauhaus University.
When researchers working for the Virtual Reality and Visualization Research Group at Bauhaus were invited to York University, Alexandro was able to work closely with them to prototype the implementation of their multi-user framework with one of the projects the GeoVA Lab had been working on. This successful collaboration inspired Alexandro to shift his research goals towards virtual reality development, and he applied for this exchange opportunity so that he could enjoy the advanced virtual reality course offered at Bauhaus. As a result of these studies, Alexandro is now tasked with adapting the educational applications he has been working on so that they may also be experienced in virtual reality.
Alexandro is also busy implementing the ‘vrEDUsys’ framework into his own Major Research Project on real-time audio analysis and visual music, with the intent of developing an application for representing remote musicians as individual music visualizations in a shared virtual reality setting. Designed to accompany live performances, this application is also intended to be used for remote educational purposes and should effectively demonstrate the capabilities of the underlying multipurpose audio analysis toolset Alexandro has been developing over the past year.
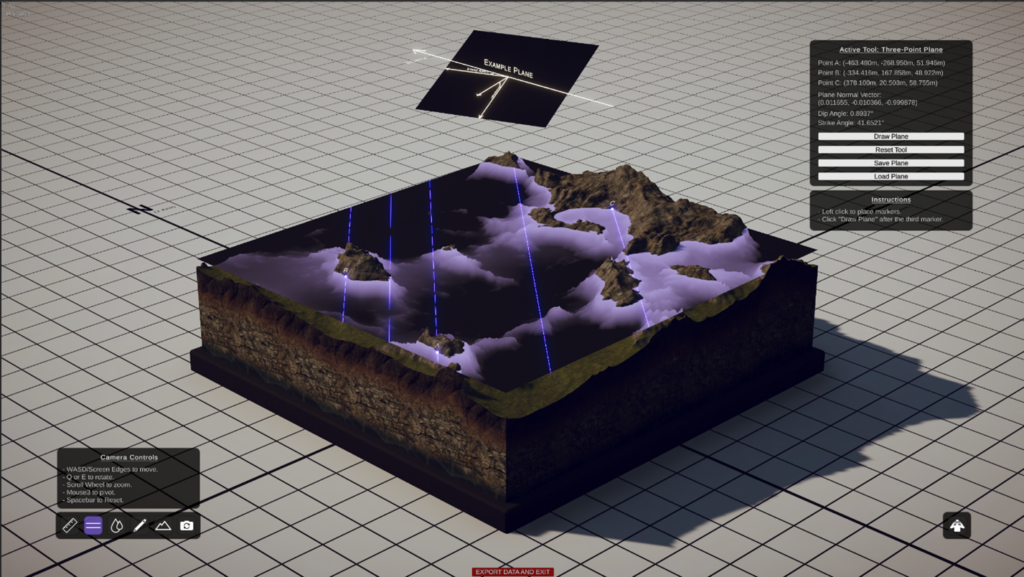
An image of the Virtual Sandbox Project, one of the projects Alexandro has been developing. This image visualizes the three-point plane problem, a fundamental concept in civil engineering and surveying that involves determining the orientation and position of a plane in three-dimensional space based on the coordinates of three non-collinear points located on that plane. This problem is crucial in various civil engineering applications, including land surveying, construction, and geodetic measurements.