About this PATHS attribute
Within the PATHS resources developed for teamwork, self-regulation and self-reflection, we have identified and incorporated opportunities for real-world connections.
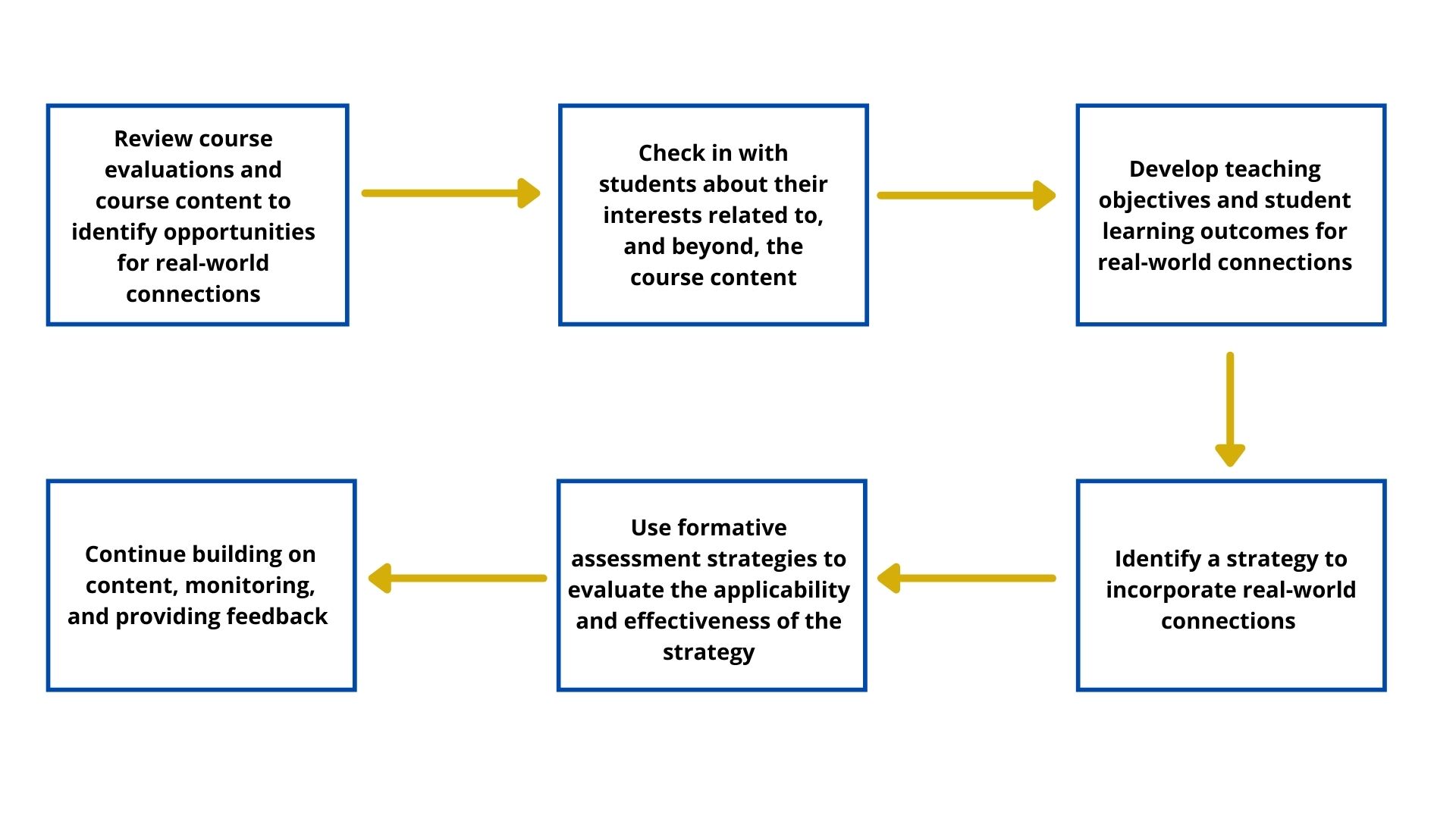
Where to start? This section offers additional information, resources, and teaching strategies that instructors can use to help students make real-world connections as they learn and gain a greater appreciation for what they are learning, and why. Follow from start to finish or pick the scenario that applies to your course.
Expand to explore

Generate engagement and deeper learning through connections
Incorporating connections between course content and real-world examples and experiences can encourage and help students develop deeper content knowledge and critical thinking skills. Making real-world connections can also cultivate curiosity and genuine interest to learn and solve problems (known as intrinsic motivation) as opposed to being motivated by external factors such as grades.
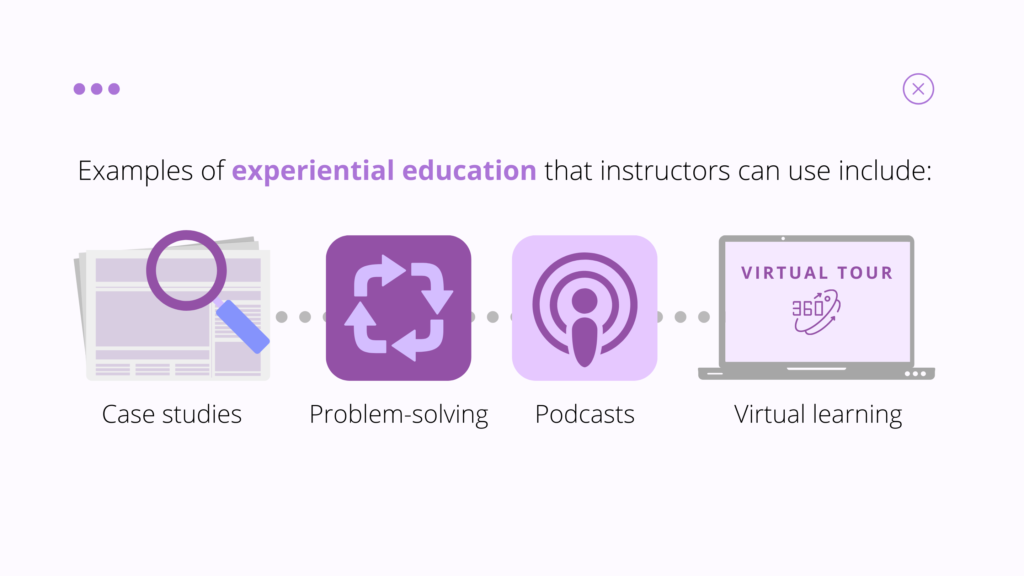
There are various strategies to include real-world connections
Opportunities to include real-world connections in a course can be made across various disciplines and in multiple learning moments. From relevant examples outside of academic and educational podcasts to inviting guest speakers and using technology to support virtual learning experiences, you can effectively include strategies that will enhance student learning. Explore examples of strategies you can incorporate and learn more about below.

Use good practices to inform your teaching plan
Use the list of good practices below as a guide and assessment tool to help you develop your plan to incorporate real-world connections.