About this PATHS attribute
Within the PATHS resources developed for teamwork, self-regulation and self-reflection, we have identified and incorporated opportunities for scaffolded learning with timely feedback.
Where to start? This section offers additional information, resources, and teaching strategies for instructors that will help students understand how their knowledge and skills are progressively developed through scaffolded learning opportunities. Follow from start to finish or pick the scenario that applies to your course.
Expand to explore

Direct students towards greater learning independence
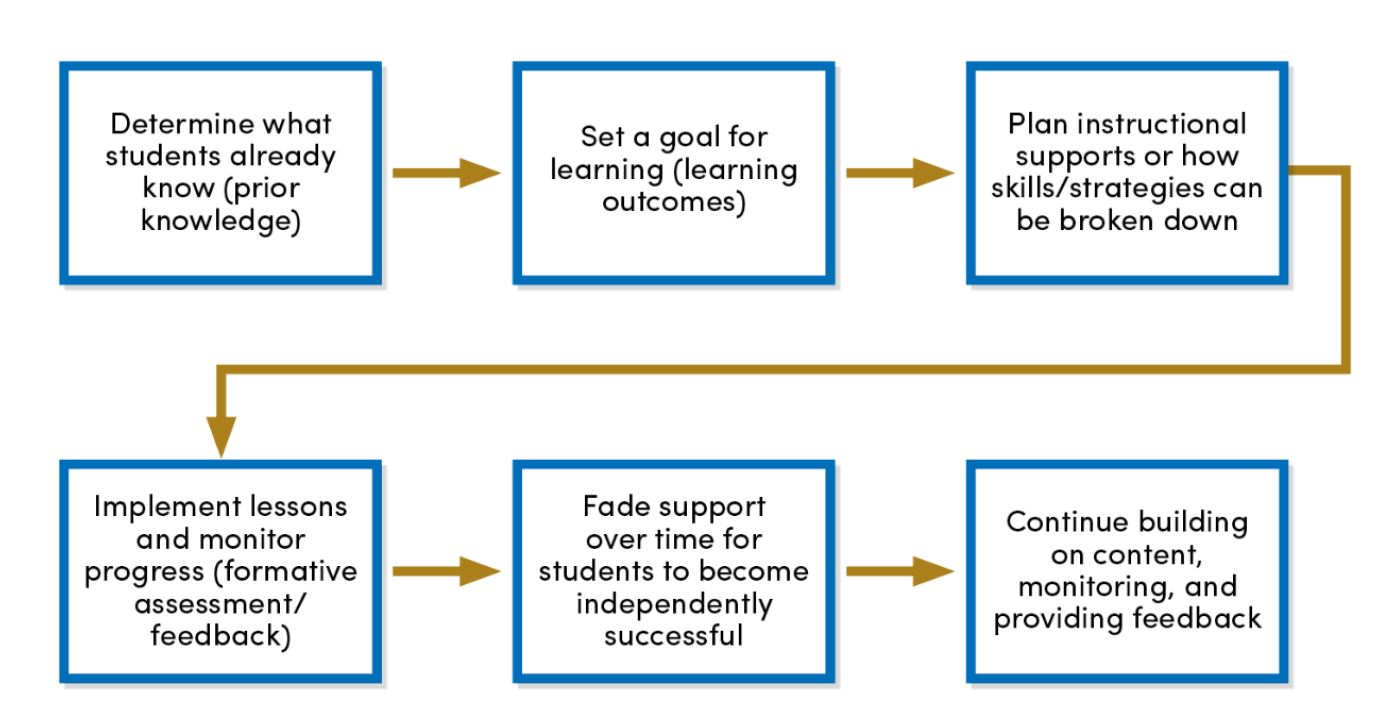
Scaffolded learning with timely feedback is an essential component of course design and teaching, effectively helping students meet course learning outcomes and directing students towards self-regulation and learning independence.
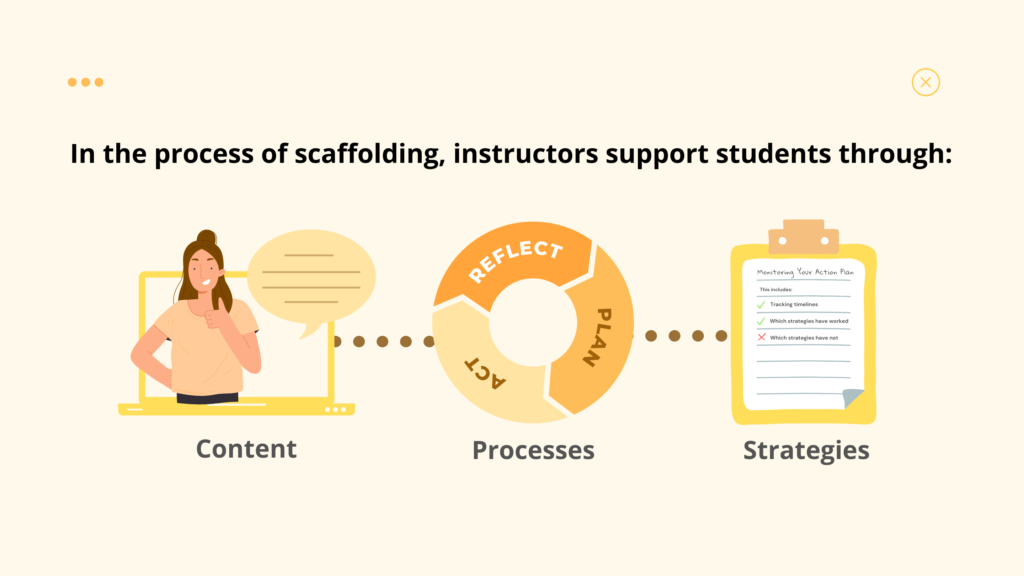
There are various strategies to scaffold student learning
Whether you are teaching physics or a health policy course, you can effectively incorporate scaffolding techniques to enhance student learning. Explore and learn more about scaffolding strategies below.

Use good practices to develop your teaching plan
Use the list of good practices below as a guide and assessment tool to help you develop a scaffolding plan.