Debuggers, MPLAB X and the Arduino
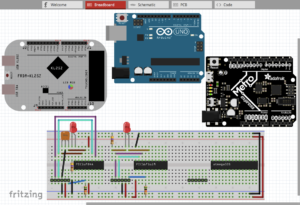
This page is about programming ATMEGA328 chips, like the one found on the Arduino UNO, using modern (post 2015) tools like MPLAB X and the Snap or PICKit4 debuggers. As of July 2021 there is a little hiccup in how to do this. Hopefully in the future Microchip will fix the issue and render this […]